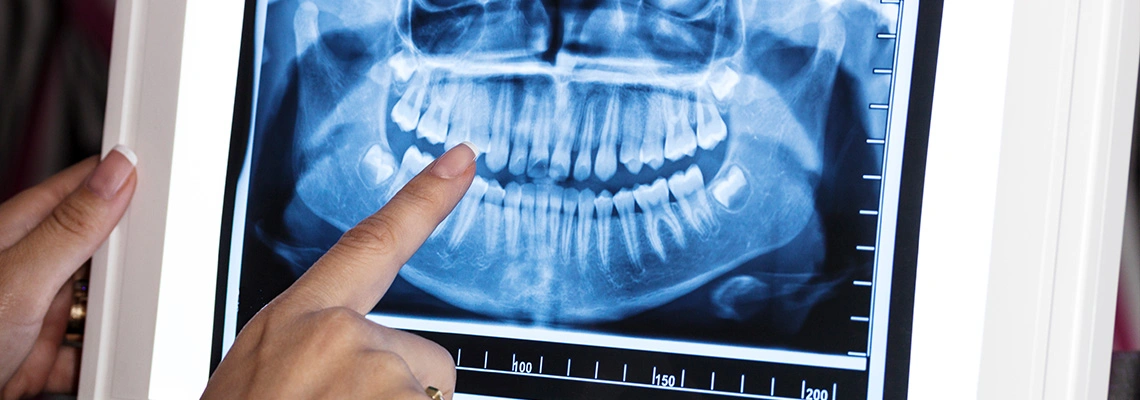
A tooth abscess known as a dental abscess is a collection of pus that forms in or around a tooth due to a bacterial infection. There are two main types of tooth abscesses: periapical and periodontal.
A periapical abscess occurs at the tip of the root of a tooth, usually as a result of tooth decay or trauma.
A periodontal abscess occurs in the gums or bones that support the tooth, usually as a result of gum disease or injury.
Table of contents:
Tooth abscess symptoms
Some of the common symptoms of a tooth abscess are:
-
Severe and persistent toothache that may radiate to the jaw, ear, or neck
-
Sensitivity to hot, cold, or sweet foods and drinks
-
Swelling and redness of the gums or face
-
Fever and general malaise
-
Difficulty opening the mouth or swallowing
-
Bad breath and unpleasant taste in the mouth
Related articles:
Tooth abscess causes
A tooth abscess is caused by bacteria that enter the tooth or the gums through a cavity, a crack, or a gum pocket. The bacteria multiply and produce toxins that irritate the surrounding tissues and cause inflammation and pus formation. The pus accumulates in a confined space and creates pressure and pain.
Tooth abscess stages
A tooth abscess can develop in different stages depending on the severity and duration of the infection:
-
In the early stage, the infection is confined to the pulp chamber of the tooth, which contains the nerve and blood vessels. The pulp becomes inflamed and painful, but the infection has not spread to the root canal or beyond.
-
In the intermediate stage, the infection spreads to the root canal and causes necrosis (death) of the pulp tissue. The infection may also reach the periapical area (the tip of the root) and form a periapical abscess. The pain may subside as the nerve dies, but the infection can still cause swelling and fever.
-
In the advanced stage, the infection breaks through the bone and forms a fistula (a small opening) in the gums or skin. The pus may drain through the fistula, relieving some of the pressure and pain. However, the infection can still spread to other parts of the mouth or body and cause serious complications.

Tooth abscess risk factors and complications
Some factors that can increase the risk of developing a tooth abscess are:
-
Poor oral hygiene and plaque buildup
-
High-sugar diet and frequent snacking
-
Smoking and tobacco use
-
Dry mouth and reduced saliva flow
-
Weak immune system or chronic diseases such as diabetes or HIV
-
Previous dental work or trauma
A tooth abscess can lead to serious complications if left untreated, such as :
-
Loss of tooth or bone
-
Spread of infection to other teeth, gums, jaw, sinuses, or brain
-
Blood poisoning (sepsis) or shock
-
Airway obstruction or difficulty breathing
Tooth abscess diagnosing
To diagnose a tooth abscess, a dentist will examine your mouth and ask about your symptoms and medical history. He may also perform some tests, such as:
-
X-rays to see the extent of the infection and damage to the tooth and bone
-
Pulp vitality test to check if the nerve of the tooth is alive or dead
-
Percussion test to tap on the tooth and see if it causes pain
-
Aspiration test to insert a needle into the abscess and draw out some pus for analysis
Tooth abscess treatment
The main goals of treating a tooth abscess are to eliminate the infection, drain the pus, and preserve the tooth. The treatment options depend on the type, location, and severity of the abscess, as well as your general health and preferences. Some of the common treatments are:
-
Antibiotics for tooth abscess: Your dentist may prescribe antibiotics to kill the bacteria and prevent the infection from spreading. However, antibiotics alone are not enough to cure a tooth abscess and should be used along with other treatments.
-
Root canal treatment: This is a procedure that involves removing the infected pulp tissue from the tooth, cleaning and shaping the root canal, filling it with a rubber-like material, and sealing it with a crown or filling. This can save the tooth and prevent further infection.
-
Tooth extraction: This is a procedure that involves removing the entire tooth from its socket. This may be necessary if the tooth is severely damaged or cannot be restored by root canal treatment. The extracted tooth can be replaced by a denture, bridge, or implant.
-
Incision and drainage: This is a procedure that involves making a small cut in the gum or skin to allow the pus to drain out. This can relieve some of the pressure and pain, but it does not remove the source of the infection. Therefore, it should be followed by root canal treatment or tooth extraction.
Tooth abscess prevention
To prevent a tooth abscess, you should practice good oral hygiene and visit your dentist regularly for checkups and cleanings. Some tips to keep your teeth and gums healthy are:
-
Brush your teeth twice a day with fluoride toothpaste and a soft-bristled brush
-
Floss daily to remove plaque and food particles from between your teeth
-
Rinse your mouth with water or an antiseptic mouthwash after eating or drinking
-
Avoid sugary foods and drinks that can cause tooth decay
-
Quit smoking and limit alcohol consumption
-
Drink plenty of water to keep your mouth moist
-
Eat a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals that support your immune system
Tooth abscess pictures

Sources:
- Tooth abscess -Symptoms & causes
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/ar/diseases-conditions/tooth-abscess/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20350907
- Dental abscess
- https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/dental-abscess/
- Tooth abscess: symptoms, causes, and treatment
- https://www.webmd.com/oral-health/abscessed-tooth