Genetic baldness or hair loss is the most common hair loss type among both men and women. Although there are several reasons behind hair loss, such as stress and anxiety, certain diseases, and medications, androgenetic alopecia is over 95% of hair loss cases in men.
In this article, we will discuss hereditary-pattern baldness, its causes and symptoms for both men and women, and treatment options.
Table of contents
Androgenetic Alopecia
Genetic hair loss is not a disease. It is a natural condition that many people suffer from after inheriting it from one of their parents. A high level of Dihydrotestosterone derived from the testosterone hormone affects the scalp negatively, shrinking and weakening the hair follicles.
Then, the growing circle of hair follicles is shortened, affecting hair follicles to become thinner and weaker, and finally, hair starts to fall out in some areas of the scalp. Furthermore. Women also can experience hereditary-pattern hair loss due to producing a high amount of (DHT).
Androgenetic Alopecia symptoms
Genetic baldness is usually diagnosed by hair loss pattern and type and the medical history of the family's person if any member suffers from androgenetic alopecia. Moreover, the doctor examines the hair scalp's patient to evaluate to what extent hair follicles are affected. The male-pattern baldness that affects men differs from the pattern which affects men in terms of the shape and infected hair areas.
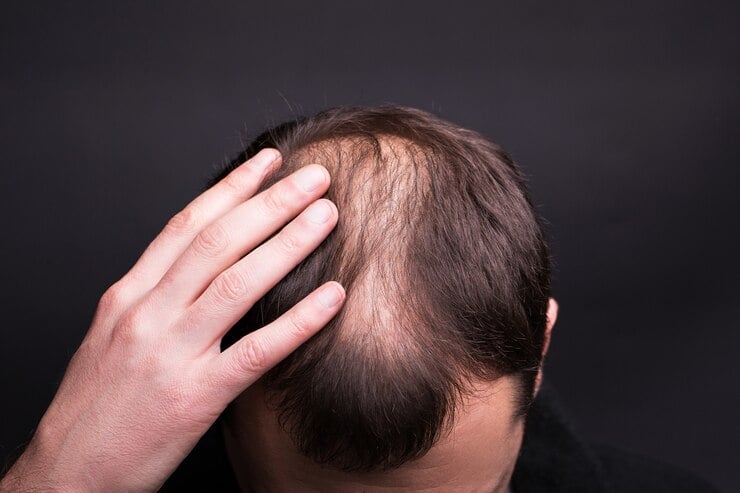

The Norwood scale is considered one of the most common classification scales to diagnose male pattern baldness cases. It works as a reference to help the doctor evaluate the patient's scalp and baldness.
The male pattern baldness starts with hairline recession at the temple. Then spreads over the vertex, taking an M-shape pattern. In some extreme cases, all of the hair is lost except for the hair on the sides and back of the scalp.
The female-pattern baldness takes a shape that differs from the one in men, and the way of diagnosing it is different too. Female-pattern loss is based on a classification scale known as Ludwig. Female baldness tends to be widespread but invisible. The hair loss begins at the top of the scalp that is the most commonly affected area by (DHT), taking the shape of a Christmas tree. Unlike men, women never experience a hairline recession, hair loss at the temples, or full baldness.
Androgenetic alopecia treatments
Generally, genetic hair loss cannot be prevented, and hair regrowth cannot be promoted. However, if the hair loss is noticed and handled in its early stages, then it might be a chance to stop or reduce it. Several options are available for fighting hair loss, such as using certain medications, taking vitamins, or following a healthy lifestyle. Finally, a hair transplant is considered a powerful option if the former ways fall to stop hair loss.
Hair loss medications
Here are the most effective medicines which play a vital role in fighting hair loss:
A medical solution that strengthens and thickens the hair follicles by increasing the blood circulation in the affected areas of the scalp. It works for both men and women and is used two times a day topically on the scalp. The final results are seen from 4 to 8 months after the application.
A medical drug that is FDA approved treats genetic hair loss by preventing testosterone from being converted to DHC, affecting the hair follicles negatively. It is taken once a day and ensures good results if used regularly. It usually has some side effects, such as headaches and skin irritation.
Following a balanced and healthy system can reduce the negative impact of (DHT) hormones on the hair follicles. Furthermore, exercising and quitting smoking can help to reduce stress, which weakens the hair follicles. It is recommended to avoid using hair bands, dye, and certain types of shampoos continuously that may affect the hair badly.
Some herbal products, such as green tea and turmeric, help treat hair loss by reducing the impact of (DHT) hormone that affects hair follicles negatively. Moreover, supplements, such as Niacin, Biotin, and other vitamins, help also treat hereditary hair loss by improving blood circulation in the scalp.
Hair transplant
Finally, hair transplantation is the best option for treating hair loss if medications or natural remedies can not respond well. Hair transplantation is a minimally invasive procedure that ensures natural and healthy hair at the same time. The operation is performed by picking hair follicles from the donor area (the back area of the scalp) and transplanting them in the bald areas (the recipient area). The operation can be done by one of those two popular techniques, (DHI) technique or (FUE) technique.